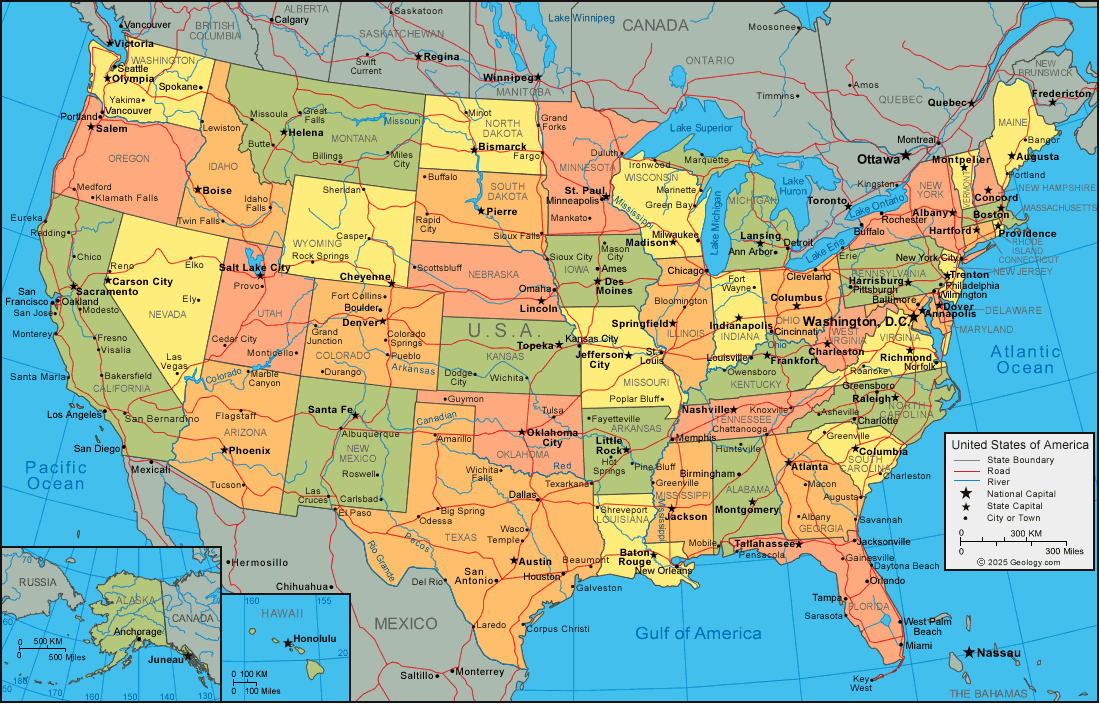
The United States of America (USA)

Paleo-Indians migrated from Eurasia to what is now the U.S. mainland at least 15,000 years ago, with European colonization beginning in the 16th century. The United States emerged from 13 British colonies located along the East Coast. Disputes between Great Britain and the colonies led to the American Revolution. On July 4, 1776, as the colonies were fighting Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War, delegates from the 13 colonies unanimously adopted the Declaration of Independence. The war ended in 1783 with recognition of the independence of the United States by the Kingdom of Great Britain, and was the first successful war of independence against a European colonial empire. The country's constitution was adopted on September 17, 1787, and ratified by the states in 1788. The first ten amendments, collectively named the Bill of Rights, were ratified in 1791 and designed to guarantee many fundamental civil liberties.
The United States is a developed country and has the world's largest economy by nominal and real GDP, benefiting from an abundance of natural resources and high worker productivity. While the U.S. economy is considered post-industrial, the country continues to be one of the world's largest manufacturers. Accounting for 34% of global military spending and 23% of world GDP, it is the world's foremost economic and military power, a prominent political and cultural force, and a leader in scientific research and technological innovations.
United States of America's Points of Interest 
1. Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon (Hopi: Ongtupqa; Yavapai: Wi:kaʼi:la, Spanish: Gran Cañón), is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in the state of Arizona in the United States. It is contained within and managed by Grand Canyon National Park, the Kaibab National Forest, Grand Canyon-Parashant National Monument, the Hualapai Tribal Nation, the Havasupai people and the Navajo Nation. President Theodore Roosevelt was a major proponent of preservation of the Grand Canyon area, and visited it on numerous occasions to hunt and enjoy the scenery.
 |
| Way too high!!! |
For thousands of years, the area has been continuously inhabited by Native Americans who built settlements within the canyon and its many caves. The Pueblo people considered the Grand Canyon ("Ongtupqa" in the Hopi language) a holy site, and made pilgrimages to it.The first European known to have viewed the Grand Canyon was García López de Cárdenas from Spain, who arrived in 1540.
2. Walt Disney World
The Walt Disney World Resort, informally known as Walt Disney World or simply Disney World, is an entertainment complex in Bay Lake, Florida (mailing address is Lake Buena Vista, Florida), near Kissimmee and Orlando and is the flagship of Disney's worldwide corporate empire. The resort opened on October 1, 1971 and is the most visited vacation resort in the world, with an attendance of over 52 million annually.

Walt Disney World is owned and operated by Walt Disney Parks and Resorts, a division of The Walt Disney Company. The property covers 27,258 acres (11,031 ha; 43 sq mi), in which it houses 27 themed resort hotels, nine non–Disney hotels, four theme parks, two water parks, four golf courses, one nine-hole walking golf course for young golfers (no electric carts allowed), two themed miniature golf courses, one camping resort, a downtown-like shopping district, and other entertainment venues. Magic Kingdom was the first and original theme park to open in the complex followed by Epcot, Disney's Hollywood Studios, and Disney's Animal Kingdom, which opened later throughout the 1980s and 1990s.
Designed to supplement Disneyland in Anaheim, California, which had opened in 1955, the complex was developed by Walt Disney in the 1960s. "The Florida Project", as he called it, was originally to be built in hopes of differential in design and scheme from Disneyland with its own diverse set of rides. Walt Disney's original plans also called for the inclusion of an "Experimental Prototype Community of Tomorrow", a planned community that would serve as a test bed for new innovations for city living. After extensive lobbying, theGovernment of Florida created the Reedy Creek Improvement District, a special government district that essentially gave The Walt Disney Company the standard powers and autonomy of an incorporated city. However, Disney died on December 15, 1966, before construction began. Without the creative mind of Disney spearheading the construction of Walt Disney World, the company instead created the resort very similar to Disneyland, just on a much larger scale, along with abandoning Walt's concept of an experimental planned community.
3. The Golden Gate Bridge
The Frommers travel guide considers the Golden Gate Bridge "possibly the most beautiful, certainly the most photographed, bridge in the world". It opened in 1937 and was, until 1964, the longest suspension bridge main spaning the world, at 4,200 feet (1,300 m).
4. The Statue of Liberty
 |
| W-O-W! |
The Statue of Liberty (Liberty Enlightening the World; French: La Liberté éclairant le monde) is a colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor in New York City, in the United States. The copper statue, designed by Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi, a French sculptor, was built by Gustave Eiffel and dedicated on October 28, 1886. It was a gift to the United States from the people of France.
The statue is of a robed female figure representing Libertas, the Roman goddess, who bears a torch and a tabula ansata (a tablet evoking the law) upon which is inscribed the date of the American Declaration of Independence, July 4, 1776. A broken chain lies at her feet. The statue is an icon of freedom and of the United States, and was a welcoming sight to immigrants arriving from abroad.
Bartholdi was inspired by French law professor and politician Édouard René de Laboulaye, who is said to have commented in 1865 that any monument raised to American independence would properly be a joint project of the French and American peoples. He may have been minded to honor the Union victory in theAmerican Civil War and the end of slavery. Due to the troubled political situation in France, work on the statue did not commence until the early 1870s. In 1875, Laboulaye proposed that the French finance the statue and the Americans provide the site and build the pedestal. Bartholdi completed the head and the torch-bearing arm before the statue was fully designed, and these pieces were exhibited for publicity at international expositions.
The torch-bearing arm was displayed at the Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia in 1876, and in Madison Square Park in Manhattan from 1876 to 1882. Fundraising proved difficult, especially for the Americans, and by 1885 work on the pedestal was threatened due to lack of funds. Publisher Joseph Pulitzer of the New York World started a drive for donations to complete the project that attracted more than 120,000 contributors, most of whom gave less than a dollar. The statue was constructed in France, shipped overseas in crates, and assembled on the completed pedestal on what was then called Bedloe's Island. The statue's completion was marked by New York's first ticker-tape parade and a dedication ceremony presided over by President Grover Cleveland.
The statue was administered by the United States Lighthouse Board until 1901 and then by the Department of War; since 1933 it has been maintained by the National Park Service. The statue was closed for renovation for much of 1938. In the early 1980s, it was found to have deteriorated to such an extent that a major restoration was required. While the statue was closed from 1984 to 1986, the torch and a large part of the internal structure were replaced. After theSeptember 11 attacks in 2001, it was closed for reasons of safety and security; the pedestal reopened in 2004 and the statue in 2009, with limits on the number of visitors allowed to ascend to the crown. The statue, including the pedestal and base, was closed for a year until October 28, 2012, so that a secondary staircase and other safety features could be installed; Liberty Island remained open. However, one day after the reopening, Liberty Island closed due to theeffects of Hurricane Sandy in New York; the statue and island opened again on July 4, 2013. Public access to the balcony surrounding the torch has been barred for safety reasons since 1916.
5. Gettysburg Battlefield
The Gettysburg Battlefield is the area of the July 1–3, 1863, military engagements of the Battle of Gettysburg within and around the borough ofGettysburg, Pennsylvania. Locations of military engagements extend from the 4-acre (1.6 ha) site of the first shot at Knoxlyn Ridge on the west of the borough, to East Cavalry Field on the east. A military engagement prior to the battle was conducted at the Gettysburg Railroad trestle over Rock Creek, which was burned on June 27.